Treating Flu In Children
Cause of flu
In general, the cause of The flu is caused by the influenza virus, which belongs to the Orthomyxoviridae family of viruses. There are several types of influenza viruses, including influenza A, B, and C. Influenza A viruses are further divided into subtypes based on the proteins on the surface of the virus, including H1N1, H3N2, and others. Influenza viruses are highly contagious and are spread from person to person through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. The virus can also be spread by touching a surface contaminated with the virus and then touching one's mouth, nose, or eyes. The flu season typically occurs during the fall and winter months, and outbreaks can occur in schools, workplaces, and other settings where people are in close contact with each other.
Read More: Be Vigilant, These Are Some Types Of Diseases That Usually Attack Children
Causes of flu in children
The causes of flu in children are the same as those in adults: the influenza virus. Children, especially those younger than 5 years old, are at higher risk for complications from the flu, such as pneumonia, dehydration, and worsening of chronic medical conditions. The flu can also cause serious complications in children with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV/AIDS.
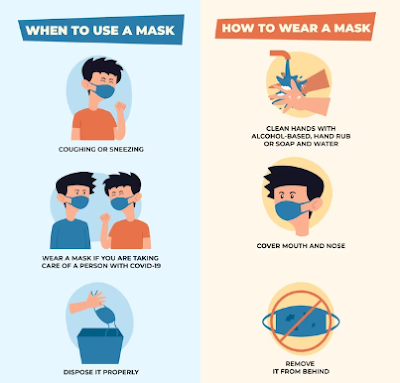
Children can catch the flu from other children or adults who are infected with the virus. The virus is spread through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Children can also catch the virus by touching a surface contaminated with the virus and then touching their mouth, nose, or eyes.
It is important to protect children from the flu by ensuring they receive an annual flu vaccine, practicing good hygiene such as washing their hands frequently, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. If a child does get the flu, it is important to seek medical attention if they develop severe symptoms or if they are at high risk for complications. Treatment for the flu in children typically involves rest, hydration, and medication to relieve symptoms.
Read More: Healthy Lifestyle Article For Students
How to treat a child who has the flu
If a child has the flu, it is important to seek medical attention if they develop severe symptoms or if they are at high risk for complications. Here are some general guidelines for treating a child with the flu:
1. Provide plenty of rest: Encourage the child to rest as much as possible. This will help their body fight off the infection and reduce the risk of complications.
2. Keep the child hydrated: Make sure the child drinks plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, or electrolyte solutions. This will help prevent dehydration, which is a common complication of the flu.
3. Control fever: If the child has a fever, you can give them acetaminophen or ibuprofen according to the instructions on the label. Never give aspirin to a child with the flu, as it can lead to a rare but serious condition called Reye's syndrome.
4. Treat other symptoms: If the child has a cough or sore throat, you can give them over-the-counter cough and sore throat remedies, but be sure to follow the instructions on the label carefully. You can also use a humidifier to help relieve congestion and cough.
5. Keep the child comfortable: Dress the child in lightweight clothing and keep the room temperature comfortable. Encourage the child to blow their nose frequently to help relieve congestion.
6. Monitor for complications: Keep an eye out for signs of complications, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or a high fever that does not respond to medication. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Remember, the best way to prevent the flu is by getting an annual flu vaccine. If a child does get the flu, be sure to take steps to prevent the spread of the virus to others, such as washing your hands frequently and covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.





0 Comments:
Post a Comment